
Last updated on : March 6th, 2020 by R Yadav
The cybersecurity panorama in India is going through an impressive phase, as current evolving cyber threats have brought the urge of sense in the enterprises to innovative tools and measures to protect themselves from cyber-attacks and cyber challenges. The cyber security needs of India are not different from those of the rest of the world but there are a lot of areas that require a unique approach in cyber security field.

Cyber Security In India 2020 : Cyber-security Policies & Initiatives
"We are sending a draft of the National Cybersecurity Strategy 2020 to a few ministries and then it will be put up to the Cabinet,” Lt. Gen Rajesh Pant, chief of the National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC) said that the vision includes- secure, safe, resilient and vibrant ICT Cyberspace for India. This cybersecurity strategy policy in January 2020 will help to achieve the goal of a $ 5 billion Indian economy.
Also Read : Effective Cybersecurity Potential Risks Predictions
“We are among the few countries that have come up with Cybersecurity policy in 2013 and conducted a gap analysis,” the top official said. The proper formation of Critical Information Infrastructure and a perfect bonding between public and private are the key aspects of a cybersecurity framework.
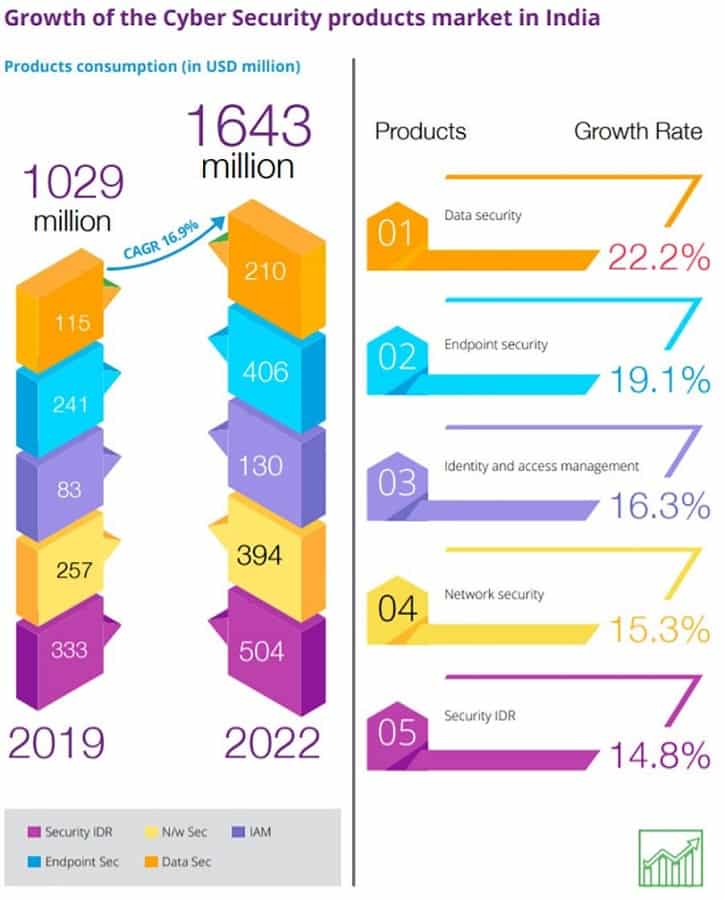
"India's cybersecurity market to touch USD 3 bn by 2022": PwC-DSCI report
India's cyber security business is expected to record 15.6% yearly growth and increase to $3 million (about Rs 21.6 billion INR ) by 2022 from $1.97 million (around Rs 14 billion INR) in 2019, according to a report. It is also estimated that the value of the digital payment transaction in India will grow annually at a rate of 20.2 percent from approximately USD 64.8 billion in 2019 to USD 135.2 billion in 2023, according to the PwC India report and the Data Security Council of India (DSCI).
As the nos. of cyber breaches has been increasing significantly across the country and especially government websites and IT infrastructure has been targeted and hacked, the need to create a secure framework for all government organizations has never been so crucial.
Cyber Security In India 2020 : Cyber-security Policies & Initiatives
In this short guide, we will list the progress and initiatives made by India and other Indian organizations to develop its cybersecurity strategy in 2020. Also, we will see Major Cyber security trends in Indian in 2020.
In order to strengthen the cybersecurity ecosystem in India, in line with the government's vision of a "digital India", the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) launched the Cyber Surakshit Bharat initiative. This program was in association with the National Electronic Government Division (NeGD).
Digitization has rapidly transformed the governance system and, therefore, the requirement of good governance is crucial. With such an initiative, it would increase awareness about cybercrime and capacity building to protect CISOs and frontline IT personnel in all government departments. In addition to raising awareness, this first public-private partnership also includes a series of workshops so that people know the best practices and help officials with cybersecurity health toolkits to address cyber threats.
Progress in the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In), which operates as the national agency to address the country's cybersecurity, has helped reduce the rate of cyber attacks on government networks. The implementation of phishing and cybersecurity awareness training in government agencies in India has helped government employees fight cybercrime. In addition to spreading awareness of the dangers posed by phishing attacks to the public, CERT-In also issues alerts and warnings about the latest cyber vulnerabilities and countermeasures to address them.
NCIIPC is a central government establishment, formed to protect the critical information of our country, which has a huge impact on national security, economic growth or public medical care. This was amended in accordance with the provisions of section 70A of the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000. This organization easily performs cybersecurity exercises to control the cybersecurity posture and the readiness of the Government and critical sectors.
The NCIIPC has broadly identified the following as "Critical Sectors":
On December 11, 2019, the Minister of Electronics and Information Technology presented the Personal Data Protection Bill in 2019 at Lok Sabha. The Bill seeks to protect the personal data of people and establishes a Protection Authority for it.
The bill governs the processing of personal data by:
(i) government,
(ii) companies incorporated in India and
(iii) foreign companies that deal with personal data of people in India.
Personal data is data that pertains to characteristics, features or identity attributes, which can be used to identify an individual. The bill classifies certain personal data as confidential personal data.This includes financial data, castes, religious, biometric data, or political beliefs, or any other category of data specified by the government, in consultation with the Authority and the corresponding sector regulator.
The bill involves the storage and processing of any critical information related to individuals only in India. It strictly states that the individual's confidential personal data needs to be stored locally, however, they can be processed abroad under certain conditions. The bill also aims to make social media companies more responsible and push them to solve problems related to the dissemination of offensive content.
In order to monitor and protect information and strengthen defenses against cyber-attacks & threats, the Govt. of Ind. launched the National Cyber Security Policy-2013 on July 2, 2013. The purpose of this framework document is to ensure safe and secure cyberspace. tough for citizens, businesses, and government With a rapid flow of information and transactions through cyberspace, a national policy was needed.
Here is the list of major cybersecurity trends for the Indian Cyber security market in 202o:
In cybersecurity, AI & ML will mature and become an integral part of the security suite. ML 0r AI-enabled solutions will be in great demand in 2020 as organizations begin to focus on anomaly detection instead of governing Detection and response-based. We have already seen the application of ML in the endpoint security space. 2020 will see ML / AI leveraged at the heart of network security, that is, an integral component of SoC (security operations centers).
IoT security will emerge as an approach in 2020. Organizations and the government will continue to adopt IoT-enabled solutions to achieve automation and efficiency, especially for critical infrastructure and smart cities. While this is happening, we should see a greater focus among those interested in securing the IoT infrastructure.
Organizations will have a renewed focus on cloud security in 2020, as cloud adoption continues to grow in 2020, attacks on the cloud shared security model will multiply. Cloud providers will have to put more resources to protect the infrastructure. In addition, there will be efforts to reinforce understanding of how to limit access to data stored in the cloud and allow only authorized personnel to access it. To address vulnerabilities and erroneous configurations, organizations will adopt technologies such as CASB (cloud access security agent) that comes with additional security controls.
As we see that the improved approach around the impact of a data breach is increasing significantly, consequently there will be a much broader approach to managing internal threats. 2020 will see organizations that cross-seize or move towards an integrated data leak prevention suite that will incorporate user and entity behavior analysis (UEBA) and the cloud access security agent (CASB).
The security testing paradigm will shift to the left, security tests will be integrated into the development cycle as the speed of commercialization becomes a key in the digital age. We will increasingly see security teams become part of the application development life cycle.
Blockchain will become the mainstream to prevent fraud and data theft: for organizations that live under the fear of fraud and identity theft in the digital economy, blockchain will show a positive side. While blockchain is expected to avoid access fraud by playing a key role in identity management, it can still remain a solid and at stake concept within startup circles. In 2020, we do not see that the identity as a service (IDaaS) based on blockchain is extended in organizations.
With the draft Personal Data Protection Act in the cabinet, the focus on data privacy will reach a turning point in 2020. Organizations will invest in aligning their infrastructure to the requirements in the bill of protection of personal data to obtain commercial advantages and avoid penalties.
Future 5G infrastructure implementations that are already in progress in India will bring new cyber threats. The 5G standard will offer a multitude of benefits, such as higher speed and performance, lower latency and better efficiency. But it will also come with risks. A greater number of devices connected to the Internet and high use of virtualization and the cloud will allow hackers to target more devices and launch larger cyberattacks. According to industry experts, the weak link in 5G security is probably communication between devices connected to the Internet. According to Gartner, the number of devices connected to the Internet will grow from 14.2 billion to 25 billion by 2021. Therefore, by 2020 you will see governments, telecommunications companies, and technology groups assembled to work on setting security standards. for 5G and the Internet of Things.
Finally, in conclusion, we can say that in 2020 India will see new growth in IT and technologies, AI, MNL, which will bring new cyber threats and vulnerabilities. But with the right Policies, initiatives & approaches, technology, and training, cybersecurity awareness should be able to keep new cyber threats and challenges at bay.
Next Topic: What is Cyber Security? Definition, Importance, Best Practices & More